INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SYSTEM:"
The word “Computer” has been derived from the Latin word “Compute” which means to Calculate
A computer is an programmable electronic device that can accept data, perform arithmetic (+,-,x,/) & logical (<,>,=,≠) operation on the data, produce the required results.
Normally, a computer is considered to be a calculating device that can perform arithmetic and logical operations at a great speed.
Components of Computer
Basically, a computer consists of four components:
i. Hardware: The physical or tangible parts of the computer called hardware. Like Monitor, Keyboard, CPU, Mouse etc.
ii. Software: The set of instructions, that tells the computer, what to do and how to do.
iii. Data: A collection of raw facts and figures is called data, which can include text, numbers, images, audios and videos etc.
iv. User: Computer cannot do any without its operator.
Information:
The processed form of data is called information. Information conveys meaning and is useful to one or more people.
Information Processing Cycle (IPC)
Information processing cycle consists of a series of tasks or steps required to convert data into information. Different steps of information processing cycle are as follows.
Characteristics of Computers.
Computers are powerful for a verity of reasons. They operate with amazing speed reliability, consistency, and accuracy. Computer can store huge amount of data and information.
Speed: Most computers carry out billions of operations in a single second. The words fastest computer can perform trillions of operations in one second.
Reliability and consistency: The electronic components in modern computers are dependable because they have a low failure rate. The high reliability of computer enables to computer to produce consistence results. So it correct & tireless machine.
Storage: Computer is used due to its large storage capacity. A data that you can place in 100 (7x4) feet almirah can be stored in a computer on a 2 x 2 inch area.
Adoptability: computer has ability to work with and to control each & every electronic device. To plug camera, motors, fax, and many other machines with it to get required results.
Categories of Computers:
There are three major ways to categories Computers.
Size & Speed: By size and speed computers divided into 4 classification, depending upon the capacity and speed of processing the data
Working Principal: By working behaviors computers divided into 3 types, depending upon the data and how computers process the data
Technology: By technology computers divided into 5 generation, each generation has different hardware manufacturing technology.
Classification of Computers (By Size & speed)
1. Micro or Personal Computers
A personal computer (PC) is a computer that can perform all of its inputs, processing, outputs and storage activities by itself. A personal computer contains a processor, memory, and one or more input, output, and storage device.
2. Mini or Midrange Computers
It is larger and more powerful computers than personal computers. It can execute five billion instructions per second. It generally consists of two or more processors. It is more reliable than desktop computer. Mini computers were introduced in 1960s. Mini computers are used in small companies to provide centralized store of information.
3. Mainframe Computers
A mainframe is a large computer in term of price, power and speed. It consists of multiple processors. It is specially designed to perform multiple intensive tasks for multiple users simultaneously. It was introduced in 1970s. A typical mainframe computer can execute 16 million instructions per second.
It is used in large organizations, such as banks, Universities and Multinational companies etc.
4. Super Computers
Super computer is the biggest in size, most expensive in price and powerful than any other computer. It can process trillions of instructions in one second. The modern super computer consists of thousands of microprocessors.
Super computers are used in weather forecasting, weapon design, preparing models of chemical and biological system, mapping the surface of the planets and studying the neural network of the brain.
Generation of Computer
Generation” in computer talk is a new step in hardware or software technology.
Different generations of computer are as follows:
| Generation |
Technology |
Description |
| 1st Generation
(1942-1955 |
 Vacuum Taube Vacuum Taube |
Vacuum tubes (fragile glass device) were the only electronic component available during those days that possible to make electronic digital computer.
These computers can calculate data in millisecond; these were very large in size.
Examples: UNIAC, EDVAC, EDSAC
|
| 2nd Generation
(1956-1964)
|
 Transistor Transistor |
The transistor (Solid State Device) a smaller and more reliable successor to the vacuum tube was invented in 1947
Faster in speed from the previous computers. These computers were able to reduce computational time from milliseconds to microseconds.
Examples: UNIVAC III, SS80, SS90, 1107
|
| 3rd Generation
(1964-1975)
|
 Integrated Circuits Integrated Circuits |
Advance “Microelectronic” technology made it possible to integrate larger number of circuit elements into very small (less than 5 mm square) surface of silicon know as Chip or Integrated Circuit(IC). The use of IC in place of transistors gave birth of new generation. they were able to reduce computational time from microseconds to nanoseconds Examples: IBM System/360 Series
|
| 4th Generation>/br>
(1975-Present)
|
 VLSI VLSI |
Small Scale Integration (SSI) contains ten to twenty ICs components. Medium Scale Integration (MSI), which has hundreds of integrated components in a single chip. Large Scale Integration (LSI) possible to integrate 30,000 components into a single chip. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) contains one million components integrated on a single chip.
|
Types of Hardware
Hardware can be categorized in the following types
| Sr.# |
Name |
Sr.# |
Name |
| 1: |
Input Device |
2: |
Output Device |
| 3: |
Processing Devices |
4: |
Storage Device |
| 3: |
Communication Devices |
INPUT
Everything that we give to the computer system through input devices is called input.
Input Devices
An input device is any hardware component that allows you to enter data or instruction into a computer..
| Sr.# |
Device |
Sr.# |
Device |
| 1: |
 Keyboard Keyboard |
2: |
 Track Ball Track Ball |
| 3: |
 Mouse Mouse |
4: |
 Glide Pad Glide Pad |
| 5: |
 Scanner Scanner |
6: |
 MicroPhone MicroPhone |
| 7: |
 Digital Camera Digital Camera |
8: |
 Webcam Webcam |
| 9: |
 Bar Code Reader Bar Code Reader |
10: |
 Joy Stick Joy Stick |
Multimedia:
Multimedia is a combination of sound and images with text and graphics. This would include movies, animation, music, people talking, sound effects like the roar of a crowd, smashing etc.
OUT PUT
Everything that computer display after processing is called output.
Types of Output:-
1: Hard Form: Printed paper or other permanent media that physically exists.
2: Soft Form: Displayed on screen or by other non-permanent means that not keep physically.
OUTPUT DEVICES
Computer hardware components that are used to receive processed information from computer are called output devices.
| Sr # |
Name |
Picture |
| 1 |
CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) Monitors
and
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) Flat-Panel Displays
|
 |
| 2 |
Speakers |
 |
| 3 |
Printers
(Impact Printers Dot Matrix Printer
(Non-Impact Printers Ink jet Printer
|
 |
| 4 |
Plotters |
 |
| 5 |
Projector |
 |
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The Microprocessor, also called the central processing unit, interprets and carries out all the basic instructions that operate the computer.


Processor contains a Control Unit (CU) and an Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU). These two components work together to perform processing of operations.
Control Unit (CU)
The control unit is the component of the processor that directs a coordinates most of operations in the computer. The control unit has a rule much like a traffic cops: it interprets each instruction issued by a program and then initiates the appropriate action to carry out the instructions.
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
The Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) another component of the processor performs arithmetic, comparison, and logical operation. Arithmetic operations include basic calculation such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Logical operation include conditions along with logical operator such as AND, OR, and NOT. For example, if only employees paid hourly can receive overtime pay, the ALU must verify to condition before computing an overtime wage:
1. The employee is paid hourly AND.
2. The employee worked more than 40 hours
Machine cycle
For every instruction, a processor repeats a set of four basic operations.
|
• Fetching
• Decoding
• Executing and if necessary,
• Storing
|
 |
Primary Storage or Main Memory (RAM) :
Primary storage, presently known as main memory or simply RAM (Random Access Memory), is the only one directly accessible to the CPU. The CPU continuously reads instructions stored there and executes them as required. Any data actively operated on is also stored there in uniform manner.
Memory stores three basic categories of data.
i. Operating system and other system software that control or maintain the computer and its devices
ii. Application programs that carry out a specific task such as word processing etc.
iii. Data to be processed by the application programs and resulting information.
RAM varies in size like 128 MB, 256 MB, 512 MB to 2 GB. RAM can not store data and instruction permanently. When we switch off the computer, all data and instructions from RAM are washed or vanished. Therefore it is called volatile memory.
ROM stands for Read only Memory. It consists of those instructions that prepare the computer for use. ROM instructions are automatically loaded into the Main Memory. These instructions cab only be read but cannot be changed or deleted. It is not possible to write new instructions into the ROM. It stores data and instructions permanently. When we switch off the computer, the instructions stored in the ROM are not lost. Therefore it is called a non-volatile memory.
SECONDARY STORAGE:
It has three types
Magnetic Disk
Magnetic Tape
Optical Disks
Magnetic Disk
It is most widely used storage media for all type of computer. A magnetic disk is a thin circular metal plate or platter coated with magnetic material. Information can be record on or read from the magnetic surface through magnetism. Magnetic disk is a random access storage media.
Types of Magnetic Disk
There are the following types of the magnetic disk
| Hard Disk |
 |
| Floppy Disk |
 |
| Zip Disk |
|
| USB flash Drive |
 |
Magnetic Tape (Sequential Access)
It is an example of old type storage media to store large amount of data permanently. Magnetic Tape consists of a thin ribbon of plastic. The tap is coated with magnetic material. The process of reading or writing of data on the tape is very slow. In magnetic tape, data can only be accessed sequentially. It is mostly used for taking backup of data
 Optical Disks
Optical disk issued laser technology to read or write information. LASER Stands for Light Amplification through stimulated emission of Radiation Laser beam is used to make tiny holes on the surface of the disk.
Compact Disk (CD )
CD is the most popular optical medium. It can hold 650 MB to 800 MB of data. The data on the CD cannot be erased like magnetic diskettes.
Optical Disks
Optical disk issued laser technology to read or write information. LASER Stands for Light Amplification through stimulated emission of Radiation Laser beam is used to make tiny holes on the surface of the disk.
Compact Disk (CD )
CD is the most popular optical medium. It can hold 650 MB to 800 MB of data. The data on the CD cannot be erased like magnetic diskettes.  DVD
DVD, also known as "Digital Versatile Disc" or "Digital Video Disc", is an optical disc storage media format. Its main uses are video and data storage. DVDs are of the same dimensions as compact discs (CDs), but store more than six times as much data
DVD
DVD, also known as "Digital Versatile Disc" or "Digital Video Disc", is an optical disc storage media format. Its main uses are video and data storage. DVDs are of the same dimensions as compact discs (CDs), but store more than six times as much data
 Motherboard
The mother board sometime called a system board is the main circuit board of the system unit. It is used to connect all kind of hardware devices.
Motherboard
The mother board sometime called a system board is the main circuit board of the system unit. It is used to connect all kind of hardware devices.  Ports: A 'port' serves as an interface between the computer and other computers or peripheral devices. Physically, a port is a specialized outlet on a piece of equipment to which a plug or cable connects.
Ports: A 'port' serves as an interface between the computer and other computers or peripheral devices. Physically, a port is a specialized outlet on a piece of equipment to which a plug or cable connects. Computer Software
Software, also called Programs. Software is a set of instructions that tells the computer what to do and how to do it.
Types of the Software
Basically there are two types of the Software
• System Software
• Application Software
System Software
System software consists of the programs that control or maintains the operations of the computer and its devices. System software serves as the interface between user, computer and application software.
There are further two types of the system software
Operating System
Utility Programs
Operating System: is a set of programs that coordinates all the activities among computer hardware devices. The operating system also contains instructions that allow users to run application software. For examples Windows, DOS, Linux, UNIX, Apple Macintosh, Sun-Solaris etc.
Utility Programs: allows a user to perform maintenance type tasks usually related to managing a computer, its devices, or its programs. For examples Antivirus, Backup and Recovery of software, Disk cleanup, Defragmenter, Drivers etc.
Application Software
Application Software consists of programs that perform specific tasks for users. Popular application software includes word processing software, spreadsheet software, database software and presentation graphics software.
Exercise
Q1. Fill in the Blanks
1. Computer derived from the ___________ word ______________.
2. The _______________ form of data is called information
3. The physical or tangible parts of the computer called _____________.
4. ___________ is the set of instructions, that tells the computer, what to do and how to do.
5. A collection of raw facts and figures is called _____________
6. Mini computers introduced in _________________.
7. IPC consists of a series of tasks required to convert ________into ______
8. When computer results are reliably the results should be __________.
9. When computer categorized according to their hardware change is called ______________.
12. Mainframe computers are also known as ____________________
13. Mini computers are also known as ________________________.
14. LCD Stands for _______________________________________.
15. Transistors invented in __________________________
16. SSD stands for ______________________.
17. Computers are divided into ____________ no of generations
18. The __________ is used in construction of IC’s
19. LSI stands for______________________________.
20. CRT stands for _______________________________.
21. Plotter is an __________________ type of device
22. Every thing that we tell to the computer is called______________.
23. The device is used to enter data & information into the computer is called _____________________.
24. Printers are __________ type of device and the results are _________form.
25. A standard Keyboard has __________ no of key.
26. CPU has _________________ and __________________ parts
27. CPU stands for______________________________.
28. _____________________ is carry’s out a program instructions.
29. Machine cycle is a series of stapes of __________, ___________, ____________, ____________.
30. 4096 Bytes equal to __________________ bits
31. PDA stands for _________________________.
32. CU stands for _________________________.
33. Numeric keypad’s ______________________________, keys use as delete key when num lock key is turned off.
34. ROM is a ____________________ memory.
35. RAM Stands for ___________________________________.
36. RAM is also known as _________________________________.
37. Outputting is process of displaying ______________________ at output device
38. The term Bit refers to the amount of memory required to store one ______.
39. IPC stands for ____________________________________________.
40. Numeric pad activates from ____________________key .
42. Because RAM is a ________________ memory, it needs a constant supply of power.
43. The term BYTE refers to the amount of memory required to store one ___.
44. __________ unit of storage is used to represent one million bytes of data
45. Monitor uses __________________________ mechanism for display
46. 256 bits = _______________________________bytes.
47. Because ROM is a ______________ memory, it doesn’t needs a constant supply of power.
48. ___________ unit of storage is used to represent one billion bytes of data.
49. Microphone is used to enter ____________________ in the computer
50. 256 byte = _______________________________bits.
51. DVD Stands for __________________________________.
Q2. True/False
1. Abacus is first computer.
2. Information is output of computer.
3. Standard keyboard has keys of 106.
4. The process of handling all operation of computer is called Processing.
5. Multimedia is a combination of text, graphics, audio and video.
6. Arrow keys, PageUp, and PageDown Keys belong to Navigation Keys.
7. Mini computers are used for multi user data share interface, but Micro computer used for multi user data processing interface.
8. 1024 trillion bytes are equal to 1048576 billion Bytes.
9. The printer that leaves its impression on paper is called impact printers.
10. A byte is equal to 23 bits.
11. 2nd Generation computers are build in the era of 1943 to 1954
12. Storing is process of storing data in ROM.
13. (13)10 is equal to (1101)2
14. Gigahertz (GHz) = I million cycle per second.
15. Hot processors make mistakes or even melt important part on the chip.
16. VDT stands for Video Display Tube
17. CRT is physical Mechanism used for the Printers.
18. Decode means converting data from machine language to human understandable language.
19. Gigahertz (GHz) = I024 million cycle per second.
20. Storage means to keep something for later use.
21. VDU stands for Video Display Unit
22. A byte is the basic unit of storage.
23. Each byte reside in the memory that identifies its location is called Word Size
24. Operating system Load in ROM when computer starts.
25. CRT is physical Mechanism used in Monitors.
26. Decode means converting data from human language to machine understandable language.
28. System software are used for facilitate the user for user office works
29. Operating system are example of system software
30. Defragmenter is example of system software.
Computer Software
Software, also called Programs. Software is a set of instructions that tells the computer what to do and how to do it.
Types of the Software
Basically there are two types of the Software
• System Software
• Application Software
System Software
System software consists of the programs that control or maintains the operations of the computer and its devices. System software serves as the interface between user, computer and application software.
There are further two types of the system software
Operating System
Utility Programs
Operating System: is a set of programs that coordinates all the activities among computer hardware devices. The operating system also contains instructions that allow users to run application software. For examples Windows, DOS, Linux, UNIX, Apple Macintosh, Sun-Solaris etc.
Utility Programs: allows a user to perform maintenance type tasks usually related to managing a computer, its devices, or its programs. For examples Antivirus, Backup and Recovery of software, Disk cleanup, Defragmenter, Drivers etc.
Application Software
Application Software consists of programs that perform specific tasks for users. Popular application software includes word processing software, spreadsheet software, database software and presentation graphics software.
Exercise
Q1. Fill in the Blanks
1. Computer derived from the ___________ word ______________.
2. The _______________ form of data is called information
3. The physical or tangible parts of the computer called _____________.
4. ___________ is the set of instructions, that tells the computer, what to do and how to do.
5. A collection of raw facts and figures is called _____________
6. Mini computers introduced in _________________.
7. IPC consists of a series of tasks required to convert ________into ______
8. When computer results are reliably the results should be __________.
9. When computer categorized according to their hardware change is called ______________.
12. Mainframe computers are also known as ____________________
13. Mini computers are also known as ________________________.
14. LCD Stands for _______________________________________.
15. Transistors invented in __________________________
16. SSD stands for ______________________.
17. Computers are divided into ____________ no of generations
18. The __________ is used in construction of IC’s
19. LSI stands for______________________________.
20. CRT stands for _______________________________.
21. Plotter is an __________________ type of device
22. Every thing that we tell to the computer is called______________.
23. The device is used to enter data & information into the computer is called _____________________.
24. Printers are __________ type of device and the results are _________form.
25. A standard Keyboard has __________ no of key.
26. CPU has _________________ and __________________ parts
27. CPU stands for______________________________.
28. _____________________ is carry’s out a program instructions.
29. Machine cycle is a series of stapes of __________, ___________, ____________, ____________.
30. 4096 Bytes equal to __________________ bits
31. PDA stands for _________________________.
32. CU stands for _________________________.
33. Numeric keypad’s ______________________________, keys use as delete key when num lock key is turned off.
34. ROM is a ____________________ memory.
35. RAM Stands for ___________________________________.
36. RAM is also known as _________________________________.
37. Outputting is process of displaying ______________________ at output device
38. The term Bit refers to the amount of memory required to store one ______.
39. IPC stands for ____________________________________________.
40. Numeric pad activates from ____________________key .
42. Because RAM is a ________________ memory, it needs a constant supply of power.
43. The term BYTE refers to the amount of memory required to store one ___.
44. __________ unit of storage is used to represent one million bytes of data
45. Monitor uses __________________________ mechanism for display
46. 256 bits = _______________________________bytes.
47. Because ROM is a ______________ memory, it doesn’t needs a constant supply of power.
48. ___________ unit of storage is used to represent one billion bytes of data.
49. Microphone is used to enter ____________________ in the computer
50. 256 byte = _______________________________bits.
51. DVD Stands for __________________________________.
Q2. True/False
1. Abacus is first computer.
2. Information is output of computer.
3. Standard keyboard has keys of 106.
4. The process of handling all operation of computer is called Processing.
5. Multimedia is a combination of text, graphics, audio and video.
6. Arrow keys, PageUp, and PageDown Keys belong to Navigation Keys.
7. Mini computers are used for multi user data share interface, but Micro computer used for multi user data processing interface.
8. 1024 trillion bytes are equal to 1048576 billion Bytes.
9. The printer that leaves its impression on paper is called impact printers.
10. A byte is equal to 23 bits.
11. 2nd Generation computers are build in the era of 1943 to 1954
12. Storing is process of storing data in ROM.
13. (13)10 is equal to (1101)2
14. Gigahertz (GHz) = I million cycle per second.
15. Hot processors make mistakes or even melt important part on the chip.
16. VDT stands for Video Display Tube
17. CRT is physical Mechanism used for the Printers.
18. Decode means converting data from machine language to human understandable language.
19. Gigahertz (GHz) = I024 million cycle per second.
20. Storage means to keep something for later use.
21. VDU stands for Video Display Unit
22. A byte is the basic unit of storage.
23. Each byte reside in the memory that identifies its location is called Word Size
24. Operating system Load in ROM when computer starts.
25. CRT is physical Mechanism used in Monitors.
26. Decode means converting data from human language to machine understandable language.
28. System software are used for facilitate the user for user office works
29. Operating system are example of system software
30. Defragmenter is example of system software.
| 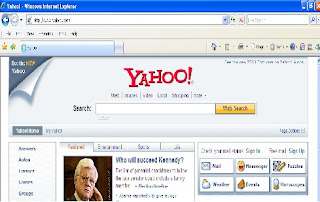 To create an Email account through you web Browser, Do as shown above click on SIGN UP :
To create an Email account through you web Browser, Do as shown above click on SIGN UP :
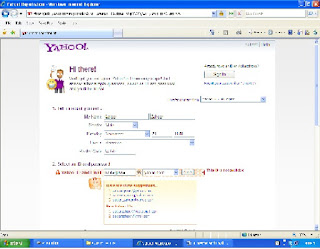 To create your E-mail account through Web Browser you have to provide some Information related to your account, for filling up a form on yahoo.com mail server.
To create your E-mail account through Web Browser you have to provide some Information related to your account, for filling up a form on yahoo.com mail server.
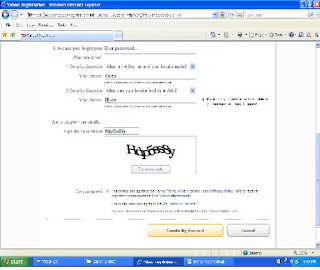 And at the end you will be asked to check the box “Do you Agree?” and then click on “Create my Account”
After clicking you will get a news message of your e-mail account and you will get this screen
And at the end you will be asked to check the box “Do you Agree?” and then click on “Create my Account”
After clicking you will get a news message of your e-mail account and you will get this screen
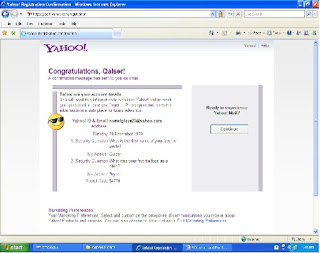 After this window click on “Continue”.
Once your e-mail account is created, you are ready to send and receive the e-mails by SIGN IN and after completing your task do not forget to SIGN OUT your e-mail account.
After you have been logged on, several options will be available to you. as shown in left circle options.
1. Inbox
After this window click on “Continue”.
Once your e-mail account is created, you are ready to send and receive the e-mails by SIGN IN and after completing your task do not forget to SIGN OUT your e-mail account.
After you have been logged on, several options will be available to you. as shown in left circle options.
1. Inbox
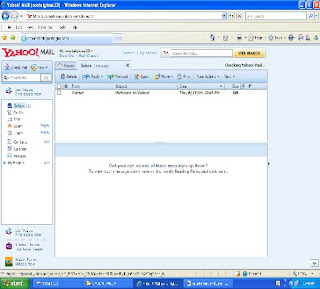 Inbox contains the new mail which you have received. From here you can read new mail, delete old mail and reply to the old messages etc.
Internet E-mail Addresses
Here is how to interpret the parts of an e-mail address:
maqsood@yahoo.com
1.maqsood--The user name of the e-mail account holder is a unique, assigned name that can be a real name, initials, a nickname, or a descriptive word such as "information."
2. @--The ‘commercial AT’ sign is required in all Internet e-mail addresses. It allows the e-mail software to distinguish between the user name and the domain name.
3. yahoo.com--The domain name identifies the company or organization of the account holder.
Major functions of Email
• Sending E-mails
Inbox contains the new mail which you have received. From here you can read new mail, delete old mail and reply to the old messages etc.
Internet E-mail Addresses
Here is how to interpret the parts of an e-mail address:
maqsood@yahoo.com
1.maqsood--The user name of the e-mail account holder is a unique, assigned name that can be a real name, initials, a nickname, or a descriptive word such as "information."
2. @--The ‘commercial AT’ sign is required in all Internet e-mail addresses. It allows the e-mail software to distinguish between the user name and the domain name.
3. yahoo.com--The domain name identifies the company or organization of the account holder.
Major functions of Email
• Sending E-mails
 • Opening an email message
• Opening an email message
 • Replying email
• Replying email
 • Forwarding email
• Forwarding email
 • Attachment of files with email.
• Attachment of files with email.


 To create an Email account through you web Browser, Do as shown above click on SIGN UP :
To create an Email account through you web Browser, Do as shown above click on SIGN UP :
 To create your E-mail account through Web Browser you have to provide some Information related to your account, for filling up a form on yahoo.com mail server.
To create your E-mail account through Web Browser you have to provide some Information related to your account, for filling up a form on yahoo.com mail server.
 And at the end you will be asked to check the box “Do you Agree?” and then click on “Create my Account”
After clicking you will get a news message of your e-mail account and you will get this screen
And at the end you will be asked to check the box “Do you Agree?” and then click on “Create my Account”
After clicking you will get a news message of your e-mail account and you will get this screen
 After this window click on “Continue”.
Once your e-mail account is created, you are ready to send and receive the e-mails by SIGN IN and after completing your task do not forget to SIGN OUT your e-mail account.
After you have been logged on, several options will be available to you. as shown in left circle options.
1. Inbox
After this window click on “Continue”.
Once your e-mail account is created, you are ready to send and receive the e-mails by SIGN IN and after completing your task do not forget to SIGN OUT your e-mail account.
After you have been logged on, several options will be available to you. as shown in left circle options.
1. Inbox
 Inbox contains the new mail which you have received. From here you can read new mail, delete old mail and reply to the old messages etc.
Internet E-mail Addresses
Here is how to interpret the parts of an e-mail address:
maqsood@yahoo.com
1.maqsood--The user name of the e-mail account holder is a unique, assigned name that can be a real name, initials, a nickname, or a descriptive word such as "information."
2. @--The ‘commercial AT’ sign is required in all Internet e-mail addresses. It allows the e-mail software to distinguish between the user name and the domain name.
3. yahoo.com--The domain name identifies the company or organization of the account holder.
Major functions of Email
• Sending E-mails
Inbox contains the new mail which you have received. From here you can read new mail, delete old mail and reply to the old messages etc.
Internet E-mail Addresses
Here is how to interpret the parts of an e-mail address:
maqsood@yahoo.com
1.maqsood--The user name of the e-mail account holder is a unique, assigned name that can be a real name, initials, a nickname, or a descriptive word such as "information."
2. @--The ‘commercial AT’ sign is required in all Internet e-mail addresses. It allows the e-mail software to distinguish between the user name and the domain name.
3. yahoo.com--The domain name identifies the company or organization of the account holder.
Major functions of Email
• Sending E-mails
 • Opening an email message
• Opening an email message
 • Replying email
• Replying email
 • Forwarding email
• Forwarding email
 • Attachment of files with email.
• Attachment of files with email.




















